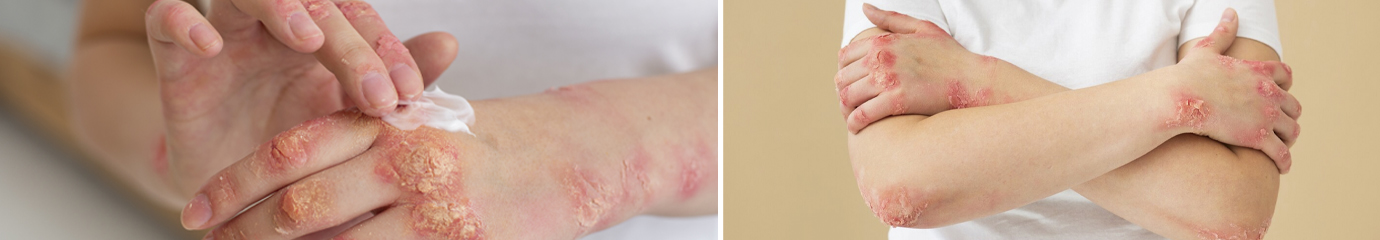
How to Manage Eczema: Top Treatment Options
A guide to understanding, treating, and preventing Eczema using proven medical and natural approaches.
Living with eczema can be a challenging and uncomfortable experience for millions of people worldwide. This chronic skin condition, characterised by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often leads to frustrating flare-ups that impact daily life. Understanding what causes eczema and exploring effective eczema treatment options are crucial steps in managing this condition and finding relief from its symptoms.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the basics of eczema, including its various types and common symptoms. We’ll explore how to create an effective eczema management plan, covering both topical and systemic treatment options. Additionally, we’ll discuss eczema on face treatment, the use of eczema treatment creams, and ways to deal with eczema dry skin. Finally, we’ll address the emotional and social aspects of living with eczema, providing valuable insights to help individuals cope with this challenging condition.
Eczema Basics: Types and Symptoms
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. While the exact cause of eczema remains unknown, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors play a role in its development.
There are several types of eczema, each with its own unique set of symptoms and triggers. The most common types include:
Atopic Dermatitis
1. Atopic dermatitis is the most prevalent form of eczema, often starting in childhood. Symptoms may include dry, itchy skin that appears red or dark brown, depending on skin tone. Affected areas typically include the creases of elbows and knees, as well as the face, hands, and scalp. Flare-ups can be triggered by environmental factors such as low humidity, cold weather, and exposure to irritants or allergens.
2. Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen, causing a localised reaction. Irritant contact dermatitis can result from exposure to harsh chemicals, soaps, or detergents, while allergic contact dermatitis is caused by an immune system reaction to substances like nickel, latex, or certain plants. Symptoms may include itching, redness, and the formation of small blisters or hives.
3. Other Forms of Eczema
Other less common types of eczema include:
Dyshidrotic eczema: This form causes small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet, especially the fingers, palms, and soles.
Neurodermatitis: Also known as lichen simplex chronicus, neurodermatitis is characterised by thick, scaly patches that result from repeated scratching or rubbing of the skin.
Nummular eczema: This type presents as round, coin-shaped spots on the skin that may be itchy, scaly, or crusty.
Seborrheic dermatitis: Primarily affecting the scalp, seborrheic dermatitis causes scaly patches, redness, and stubborn dandruff.
Stasis dermatitis: This form of eczema occurs due to poor circulation in the lower legs, leading to swelling, itching, and skin discoloration.
Regardless of the type, eczema can cause significant discomfort and may lead to complications such as skin infections if left untreated. Proper eczema diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. This may involve identifying potential triggers, such as environmental allergens or irritants, and taking steps to avoid them.
Eczema treatment often focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving itching, and restoring skin hydration. Topical corticosteroids are commonly used to manage flare-ups, while moisturisers and gentle skincare routines help maintain skin health between episodes. In some cases, oral medications or light therapy may be recommended for more severe or persistent cases.
With proper care and attention, it is possible to minimise the impact of eczema and maintain healthy, comfortable skin.
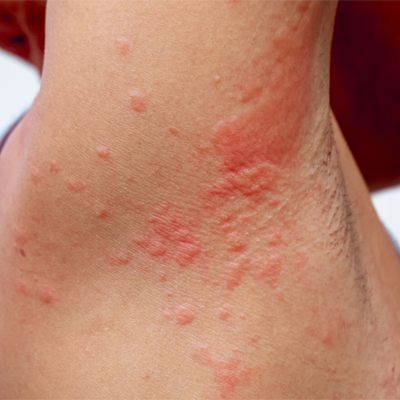
Creating an Effective Eczema Management Plan
Creating an effective eczema management plan is crucial for controlling symptoms and minimising the impact of this chronic skin condition on daily life. A comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of eczema can help individuals achieve better outcomes and improve their quality of life.
Working with a Dermatologist
One of the first steps in developing an effective eczema management plan is to work closely with a dermatologist. A dermatologist can provide an accurate diagnosis, which is essential for determining the best course of treatment. They can also offer guidance on identifying and avoiding triggers, recommend appropriate skin care products, and prescribe medications when necessary.
During your initial consultation, be sure to discuss your medical history, current symptoms, and any factors that seem to worsen your eczema. This information will help your dermatologist develop a personalised treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Regular follow-up appointments are also important for monitoring your progress and making any necessary adjustments to your treatment regimen.
Identifying Personal Triggers
Eczema triggers can vary from person to person, so it’s essential to identify your own personal triggers as part of your management plan. Common triggers include stress, certain foods, environmental allergens, and irritants such as harsh soaps or detergents. Keeping a symptom diary can be a helpful tool for tracking flare-ups and identifying potential triggers.
Once you’ve identified your triggers, take steps to minimise your exposure whenever possible. This may involve making changes to your diet, using hypoallergenic products, or implementing stress-reduction techniques. If environmental allergens are a significant trigger for you, consider using an air purifier or dehumidifier to help control indoor allergens and maintain optimal humidity levels.
Developing a Daily Skincare Routine
Cleanse gently: Use lukewarm water and a mild, fragrance-free cleanser. Pat skin dry.
Moisturise frequently: Apply a moisturiser formulated for sensitive skin throughout the day.
Consider medicated creams: Your dermatologist may recommend a corticosteroid cream for flare-ups.
Avoid irritants: Limit hot showers, harsh soaps, and low humidity. Use a humidifier and wear breathable clothing, ideally cotton..
In addition to your daily skincare routine, be mindful of other factors that can impact skin hydration, such as hot showers, harsh soaps, and low humidity environments. Use a humidifier in your home or workplace to help keep the air moist, and wear loose, breathable clothing to minimise irritation and overheating.
By working closely with a dermatologist, identifying personal triggers, and developing a consistent skincare routine, individuals with eczema can take control of their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Remember that managing eczema is an ongoing process, and it may take some trial and error to find the right combination of strategies that work best for you. With patience, persistence, and a comprehensive approach, however, it is possible to effectively manage this challenging skin condition.
Topical and Systemic Treatment Options
Topical corticosteroids are a cornerstone of eczema treatment, as they effectively reduce inflammation, itching, and rash. They come in various potencies and formulations, including ointments, creams, lotions, and sprays. Low-potency steroids are generally used on sensitive areas like the face, while higher potencies are reserved for thicker skin or more severe flare-ups. Proper use is crucial to avoid side effects such as skin thinning, stretch marks, and acne.
A newer option is the topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, ruxolitinib cream, approved for short-term, non-continuous treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 12 years and older who have not responded adequately to other topical therapies. By blocking specific enzymes involved in inflammation, itch, and skin barrier function, ruxolitinib reduces the severity of eczema signs and symptoms. An oral JAK inhibitor is also now available RINVOQ (upadacitinib).
When topical treatments fail to control eczema or the condition is severe, systemic medications may be necessary. Oral corticosteroids, like prednisone, rapidly improve symptoms but are only used short-term due to potential side effects. Immunosuppressants, such as cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate mofetil, work by reducing the body’s immune response. While effective, they require close monitoring for side effects, including increased infection risk, liver and kidney problems, and rarely, skin cancer or lymphoma.
Dupilumab, an injectable biologic medication, has revolutionised the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. By targeting specific inflammatory pathways, it significantly improves eczema symptoms and quality of life. Other biologics, such as tralokinumab and lebrikizumab, are also showing promise in clinical trials.
Phototherapy, particularly narrowband UVB, can be an effective second-line treatment for widespread eczema. It involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of UV light, which has anti-inflammatory effects. However, it requires regular treatments and carries a slightly increased risk of skin ageing and cancer with long-term use.
Choosing the best eczema treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, and the location of affected skin. A personalised approach, often combining topical and systemic therapies, is essential for optimal management of this challenging skin condition. Working closely with a dermatologist can help identify triggers, maintain skin hydration, and prevent flare-ups, leading to improved outcomes and quality of life for those living with eczema.
Coping with Eczema: Emotional and Social Aspects
Living with eczema can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being and social interactions. The constant itching, discomfort, and visible symptoms can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and isolation. However, there are strategies that can help individuals cope with the emotional and social challenges of eczema.
Dealing with Stress and Anxiety
Having a strong support network is crucial for individuals with eczema. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with the condition can provide a sense of validation and reduce feelings of isolation. Support groups, whether in-person or online, offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, seek advice, and find encouragement.
Family and friends can also play a vital role in providing emotional support. It’s important for individuals with eczema to communicate openly with their loved ones about their needs and how they can best offer support. This may involve educating family and friends about the condition, setting boundaries, and asking for help when needed.
Improving Quality of Life
While eczema can have a significant impact on quality of life, there are steps individuals can take to minimise its effects. One key aspect is maintaining skin hydration through the use of moisturisers and gentle skincare routines. Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods or environmental allergens, can also help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Engaging in activities that boost self-esteem and promote a positive body image can be beneficial for individuals with eczema. This may include practising self-compassion, focusing on personal strengths and accomplishments, or participating in activities that make them feel confident and empowered.
It’s also important for individuals with eczema to advocate for themselves in social and professional settings. This may involve educating others about the condition, setting boundaries, and requesting accommodations when necessary. By taking an active role in managing their eczema and its impact on their life, individuals can improve their overall quality of life.
In conclusion, coping with the emotional and social aspects of eczema requires a multifaceted approach. By managing stress, building a strong support network, and taking steps to improve quality of life, individuals with eczema can better navigate the challenges of living with the condition. Remember, seeking support from healthcare professionals, such as dermatologists or mental health specialists, can also be an important part of the journey towards improved emotional well-being and social functioning.
Conclusion
Managing eczema effectively requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments with lifestyle adjustments. This article has explored various aspects of eczema management, from understanding the basics of the condition to creating a personalised treatment plan. By working closely with healthcare providers, identifying triggers, and maintaining a consistent skincare routine, individuals with eczema can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Living with eczema has an impact on both physical and emotional well-being, but with the right strategies, it’s possible to cope with these challenges. Stress management techniques, building a strong support network, and advocating for oneself in social and professional settings are crucial steps to take control of the condition. Remember, while eczema can be a lifelong condition, advances in treatment options and management strategies offer hope for better symptom control and improved overall health.
FAQs
What is the most effective way to treat eczema?
There is no single ‘most effective treatment’ as responses typically vary from person to person. However, topical corticosteroids are widely recommended for treating various types of eczema as they help reduce inflammation and alleviate itching, allowing the skin to heal.
How should eczema be managed effectively?
To manage eczema effectively, it’s essential to moisturise the skin two to three times daily. Choose moisturisers that are free from alcohol, scents, dyes, fragrances, parabens, and other irritants. Using a clean humidifier at home can also be beneficial.
What does a typical treatment plan for eczema include?
A standard treatment plan for atopic dermatitis often begins with regular moisturising and adopting other self-care practices. If these measures are insufficient, healthcare providers may recommend medicated creams to control itching and help repair the skin, sometimes in combination with other treatments.

