
Effective Wart Removal: Top Medical and Natural Remedies
A comprehensive guide to understanding, treating, and preventing warts using proven medical and natural approaches.
Warts can be a persistent and embarrassing skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These small, rough growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) often appear on hands, feet, and other areas of the body, prompting many to seek effective wart removal methods. From over-the-counter treatments to professional medical procedures, there are numerous options available to tackle this common skin issue.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore various wart removal techniques, including medical treatments like cryotherapy and laser wart removals. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of different approaches, from wart removal creams to plantar wart removal methods, to help you make an informed decision about the best course of action for your specific situation. Additionally, we’ll cover prevention strategies and signs that indicate when it’s time to consult a healthcare professional for more advanced treatment options.
Understanding Warts: Causes and Types
What are warts?
Warts are small, rough growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These non-cancerous bumps can appear on various parts of the body and come in different forms. While warts are very common and usually harmless, they can be bothersome and sometimes painful. Most people will experience a wart at some point in their lives, with children and teenagers being the most susceptible.
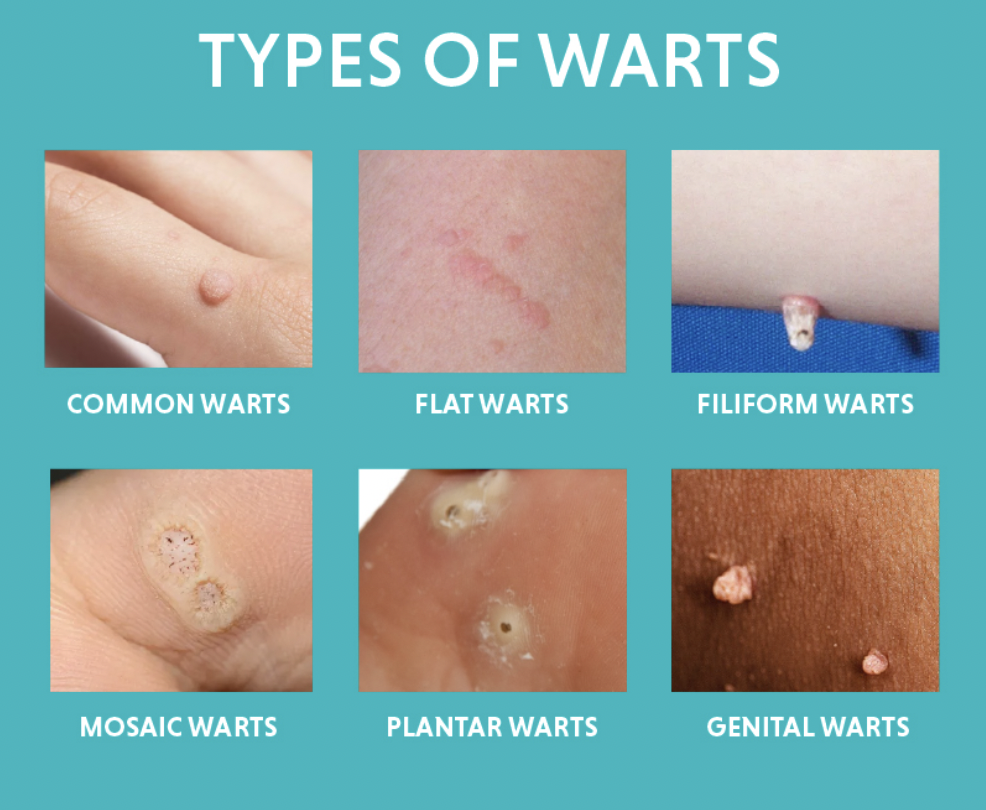
Common types of warts
There are several types of warts, each with distinct characteristics and preferred locations on the body.
- Common warts (verruca vulgaris) typically appear on the fingers, hands, knees, and elbows. They have a rough, thick, and grainy appearance with a rounded top, sometimes resembling a cauliflower.
- Plantar warts grow on the soles of the feet. Unlike other warts, they grow inward due to the pressure from walking, which can cause discomfort.
- Flat warts are small, smooth, and slightly raised, often appearing in clusters on the face, hands, or lower legs.
- Filiform warts are finger-like projections that typically grow near the mouth, eyes, or nose.
- Mosaic warts are clusters of small, flat warts that appear on the hands or soles of the feet.
- Genital warts affect the genital area and are transmitted through sexual contact.

How warts spread
Warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching objects that have come into contact with the virus, such as towels or razors. The virus thrives in warm, moist environments like public showers or swimming pools. Warts can also spread from one part of the body to another through scratching or picking at the growths.
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing organ transplants, are more susceptible to developing warts. Other risk factors include frequent contact with raw meat, communal showers, or having family members with warts. While most warts will eventually go away on their own, the process can take months or even years. Fortunately, there are many effective wart removal options available, including over-the-counter wart removal creams, cryotherapy, and laser treatments. If you have persistent or painful warts, consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of action for your specific case.
Medical Treatments for Wart Removal
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is one of the most common medical treatments for wart removal. It involves freezing the wart using liquid nitrogen, which causes the wart tissue to die and eventually fall off. The procedure is usually performed by a dermatologist or other healthcare provider and can be done in a single office visit.
During the treatment, the liquid nitrogen is applied directly to the wart using a spray or cotton swab. The freezing process may cause some discomfort or pain, but it is generally well-tolerated. After the treatment, a blister may form over the wart, which will eventually dry up and fall off, taking the wart with it.
Cryotherapy is most effective for small, isolated warts and may require multiple treatments for larger or more stubborn warts. Side effects can include temporary pain, swelling, and blistering at the treatment site.
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is a common ingredient in many over-the-counter wart removal creams and gels. It works by gradually peeling away the infected skin, allowing the wart to be removed layer by layer.
Salicylic acid products are available in various strengths, ranging from 17% to 40%, and can be applied directly to the wart. To use salicylic acid for wart removal, the affected area should be soaked in warm water to soften the skin, and then the product should be applied and covered with a bandage. This process is repeated daily until the wart is gone, which can take several weeks or even months.
Salicylic acid is most effective for small, flat warts and may not be as effective for larger or deeper warts. It can also cause skin irritation in some people, so it is important to follow the instructions carefully and discontinue use if any adverse reactions occur.
Electrocautery and curettage
Electrocautery and curettage is a surgical procedure that involves burning the wart with an electric current and then scraping it off with a curette, a special surgical instrument. This method is usually reserved for larger or more stubborn warts that have not responded to other treatments.
The procedure is performed under local anaesthesia and may cause some discomfort or pain during and after the treatment. After the wart is removed, the area is usually covered with a bandage to promote healing and prevent infection.
Electrocautery and curettage has a high success rate for wart removal, but it can also cause scarring and may not be suitable for all types of warts or all areas of the body.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is a newer method of wart removal that uses a focused beam of light to destroy the wart tissue. There are several types of lasers that can be used for this purpose, including pulsed dye lasers and CO2 lasers.
During the procedure, the laser is directed at the wart, and the heat from the laser destroys the blood vessels that supply the wart, causing it to die and fall off. Laser wart removals may require multiple treatments to be effective and can be more expensive than other methods. However, it can be a good option for people who have not had success with other treatments or who have warts in hard-to-treat areas.
Side effects of laser therapy can include temporary pain, swelling, and redness at the treatment site, as well as a small risk of scarring.
Prevention and When to See a Doctor

Hygiene practices
- Wash hands thoroughly: Especially after touching warts or potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Don’t share personal items: This includes towels, razors, and socks.
- Keep warts covered: Use a bandage to prevent spreading.
- Avoid touching warts: Don’t pick or scratch them.
- Wear shoes in public areas: Protect your feet in showers, locker rooms, and pool areas.
HPV vaccination
The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect against certain strains of the human papillomavirus that can cause warts and other health problems. The vaccine is typically recommended for children and young adults, with the ideal age for vaccination being 11-12 years old.
The HPV vaccine is administered in a series of shots over several months. It’s important to complete the entire series to ensure maximum protection against the virus. While the vaccine is most effective when given before an individual becomes sexually active, it can still provide benefits for those who are already sexually active.
In addition to preventing warts, the HPV vaccine also offers protection against cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers caused by certain strains of the virus. Talk to your healthcare provider about whether the HPV vaccine is appropriate for you or your child.
Signs that require medical attention
While most warts are harmless and will eventually go away on their own, there are certain situations where it’s important to seek medical attention. If you have a wart that is painful, bleeding, or interfering with your daily activities, make an appointment with your healthcare provider or a dermatologist.
If you have a weakened immune system due to a condition like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or cancer treatment, you may be more susceptible to developing warts and other infections. In these cases, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare team to monitor any skin changes and promptly address any concerns.
If you have a wart that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter wart removal creams or other home remedies after several weeks of treatment, it’s time to consult a professional. Your dermatologist can recommend more aggressive treatment options like cryotherapy or laser wart removals to effectively eliminate stubborn warts.
Remember, while most warts are benign, some skin growths can be a sign of a more serious condition like skin cancer. If you notice any unusual changes in your skin, such as a rapidly growing or irregularly shaped lesion, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist right away for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
Wart removal is a common concern for many people, and this guide has explored various methods to tackle this issue. From medical treatments like cryotherapy and laser wart removals, there are many options to choose from. The choice of treatment depends on factors like the type and location of the wart, personal preferences, and the advice of healthcare professionals.
Prevention plays a key role in managing warts. Boosting the immune system, practising good hygiene, and considering HPV vaccination are essential steps to reduce the risk of developing warts. While most warts are harmless and often go away on their own, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if they cause pain, bleed, or don’t respond to home treatments.
Remember, persistent or unusual skin growths should always be checked by a dermatologist to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.

